This week, we launched our report Medtech and the Internet of Medical Things: How connected medical devices are transforming health care. Our report takes an in-depth look at how connectivity is impacting the medtech industry, the challenges and opportunities that medtech companies are facing due to the rise of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), the specific role connected medical devices are playing in the growth of the IoMT and what the future will bring for medtech and the IoMT.
Medical devices are everywhere; most patient interactions with the health care system involve devices and equipment made by medtech companies. Over 500,000 types of these devices exist, including wearables (skin patches, insulin pumps and blood glucose monitors), implantables (pacemakers and cardioverter defibrillator devices) and stationary medical devices (home monitoring services, connected imaging devices and scanning machines).
Major advances in wireless technology, miniaturisation and computing power are driving innovation in medtech. This is leading to the development of an increasing number of connected medical devices that are able to generate, collect, analyse and transmit health data or images, and connect to health care provider networks, transmitting data to either a cloud repository or internal servers. These connected devices, along with the data they produce, IT systems and software, and connectivity technologies and services, are combing to create the IoMT, which can impact health care in numerous ways (see Figure 1).
Figure 1. The benefits of the IoMT

MarketsandMarkets valued the IoMT market at $41.2 billion in 2017 and expects it to rise to $158.1 billion in 2022. This growth will occur in all regions of the world and across all the different segments of the market (see Figure 2).
Figure 2. Significant IoMT market growth is predicted

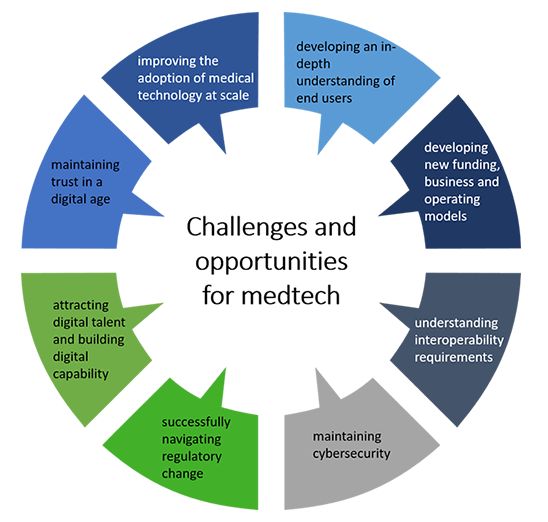
The rise in the IOMT comes at a time when health care is becoming increasingly expensive. Global health care spending is expected to grow 4.2 per cent per year, from $7.1 trillion in 2015 to $8.7 trillion by 2020, due largely to the fact that more people are living longer but with multiple comorbidities. Consequently, health care risks becoming unaffordable in many countries if these rising costs persist. The medtech industry has a key role to play in helping to improve the quality and efficiency of care and support the delivery of more cost-effective care. The ability of connected devices to generate health data is critical to the shift to value-based care (VBC). However, medtech also faces a number of opportunities and challenges that need to be addressed if the full value of the IoMT is to be realised (see Figure 3).
Figure 3. Challenges and opportunities for medtech
Creating the IoMT at scale requires close collaboration with patients, providers, payers, pharma and other medtech manufacturers. Our research identified multiple ways that medtech is utilising the power of the IoMT to transform health care. Our report features several case studies that provide evidence of how the following key enablers are driving the transformation of health care:
- collaboration between health care providers and medtech – these collaborations allow all stakeholders to improve their understanding of patient needs and deliver more proactive, cost-effective care
- connected medical devices benefitting patients, providers and payers – being able to quantify, contextualise and communicate data generated on a patient's condition and the effectiveness of the health care providers operations allows the medtech industry to provide solutions that deliver value to both the patient and provider
- joining the dots between connected medical devices and health care IT systems – linking disparate sets of data that sit within health care organisations is central to achieving connectivity, data acquisition and analytics at scale
- applying advanced analytics to provide critical insights and empower better decision-making – insight generated from mining, managing and analysing data can play a key role in aiding health systems to reduce costs and improve quality, identify populations at risk, connect with consumers and better understand performance
- medtech services that demonstrate improvements in patient outcomes and reduce health care costs – service orientated solutions that support the tenants of VBC are improving patient outcomes and reducing the costs of health care, transforming medtech companies from a manufacturer to a health care provider.
As we look to the future, cost-effective and purposefully-designed, technology-enabled health care solutions will improve the well-being of millions of people and radically change the way services are delivered to patients. For this to occur, medtech companies and will need to capitalise on the possibilities presented by the IOMT and the new models of health care that are emerging, including VBC and population health management (PHM). These changes will help connect patients with providers and payers, and enable providers and payers to become more patient centric, productive and cost effective.
More specifically, connected medical devices are a key enabler across the six predictions made in our November 2017 report The future awakens: Life sciences and health care predictions 2022. The extent to which the predictions are realised is heavily dependent on the continued innovation and adoption of connected medical devices at scale. Moreover, in realising the predictions, current boundaries between the IoMT and consumer IoT will start to blur, giving rise to new opportunities for medtech companies.
Furthermore, technologies such as AI, machine learning, robotics, 3D printing and voice technology are creating new opportunities for medtech companies, while at the same time changing ways of working across the whole IoMT ecosystem. A growing number of medtech companies are capitalising on these trends to develop service-oriented solutions that support VBC, aligned to the therapeutic expertise and specialised products of the organisation. Consequently, these medtech companies are maintaining high-quality patient outcomes while reducing costs compared to similar services run by traditional health care providers.
Other companies are utilising IoMT capabilities to aggregate data and offer consultative services and predictive analytics, including opening up health data to organisations that have typically found it difficult to gain access to data outside of their own organisation. These and other developments provide clear opportunities for medtech companies to transition from a provider of innovative products to an insightful partner in health care (see Figure 4).
Figure 4. Connected medical devices are helping medtech companies transition from innovative product suppliers to insightful partners in health care

The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.
