As is well known, high-quality patents may bring huge benefits to an enterprise, at the same time, the enterprise's continuous investment in patents is needed to obtain these benefits. The enterprise has to invest not only time, but also real money. The enterprise's patent investments mainly focus on two aspects: first, research and development, and second, patent prosecution and maintenance. Usually for an enterprise that seeks long-term development, it is unlikely to reduce the cost of research and development. In such case, is it possible to reduce the cost of patent prosecution and maintenance?
The cost of patent prosecution and maintenance comes down to two aspects: first, official fees, and second, the enterprise's internal expense and the agency's service fees. Regardless of whether the enterprise can enjoy the reduction or postponement of official fees, the official fees are generally fixed. The only possibility of cost reduction is to reduce the enterprise's internal expense and the agency's service fees. However, it would not be appropriate to simply reduce staff or shorten the process, because this may lead to quality degradation or process risks. Therefore, technical innovation is considered to appropriately reduce cost, for example, the enterprise may review which work can be replaced or at least partially replaced by artificial intelligence (AI), thereby reducing enterprise cost by utilizing AI.

At present, a relatively mature AI technology for handling patent matters is machine translation using neural network technology. The quality of machine translation has been significantly improved more than ever before, and the translation results are sufficient for reference purposes, so it is believed that appropriate use of machine translation will greatly reduce enterprise cost.
To analyze how to utilize machine translation, let's first check the requirements on translation in patent matters. According to requirements on translation accuracy, documents to be translated during the patent prosecution and maintenance processes can be divided into two types: legal documents, and reference materials.
Legal document translation refers to translation of documents with legal effect, which involves outlining the patent right, and thus requires high translation accuracy. For legal documents, in order to ensure the translation accuracy, human translation is needed. Generally, the human translation process is not completed in one step, and it may involve translation, revision, proofreading and double checking. In this procedure, the longer the translation process, the higher the translation cost. Therefore, machine translation, instead of human translation, may be used for the first step to reduce cost and improve translation efficiency, whilst a subsequent human revision step ensures the translation accuracy. That is, machine translation combined with human revision is applicable to the translation of legal documents.
Reference material translation refers to translation of reference materials cited in the patent prosecution and maintenance process. Generally, the reader only needs to know the general content of the reference materials and does not require the translation accuracy to be as high as legal document translation. Moreover, when reading reference materials, the reader often wants to obtain instant translation results. Therefore, machine translation is more appropriate for reference materials.
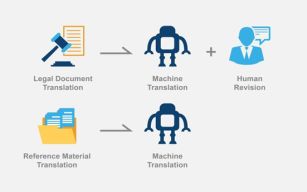
The analysis above shows that legal documents require machine translation combined with human revision, and for reference materials machine translation is enough. So, as for translation demands in the patent prosecution and maintenance process, which apply to legal document translation and which apply to reference material translation? Let's analyze it stage by stage:
1. Technology Research and Development Stage
In the research and development process, technicians need to learn about the existing technologies in the art, both domestic and abroad. A common way is to read patent documents. When reading patent documents in foreign languages, it is inevitable to encounter language barriers. Human translation is costly and time consuming. In addition, readers may desire instant translation results. Therefore, such translation demand belongs to reference material translation, and machine translation is applicable.
2. Patent Mining Stage
In the process of patent mining, an in-house counsel of an enterprise usually needs to learn about the existing technologies and perform a novelty search. The search results usually involve a large number of patent documents, which certainly include patent documents in foreign languages. At this time, the demand of the in-house counsel of the enterprise is to quickly understand the general content of the patent documents in foreign languages. Therefore, such translation demand applies to reference material translation, and machine translation is applicable.
3. Patent Application Document Preparation Stage
Patent application documents are the most important legal documents. The application documents themselves decide the possibility of a patent grant in the future and the scope of the patent right. Thus, translation of patent application documents applies to legal document translation. This process generally involves text translation and adaptation in legal formality. For text translation, machine translation is applicable to the first translation step; and adaptation in legal formality requires an agent to adjust the application documents according to the local patent law and the applicant's strategy, and thus requires human work. Therefore, translation at this stage can be completed through machine translation combined with human revision.
4. Patent Examination Stage
At this stage, the examiner issues notifications of office action after examining the patent application documents. For a foreign applicant, translation of the notifications of office action is needed to make it understandable to the applicant. Similarly, if Chinese reference documents are cited, translation of the reference documents is also needed. Both the notifications of office action and reference documents can be considered as reference materials. Therefore, such translation demands apply to reference material translation, and machine translation is applicable.
In addition, there are differences in patent procedures in different countries. For example, USPTO requires documents for IDS, and this also applies to reference material translation, and machine translation is applicable.
5. Patent Invalidation Stage
In the process of patent invalidation, search is the first necessary stage, that is, prior art documents, especially patents, serving as reference documents should be found through a search. In the invalidation search process, a huge number of prior art documents may be involved. The translation of these prior art documents involved at this stage applies to reference material translation, and machine translation is applicable.
In China, if a reference document in a foreign language has been determined as evidence for requesting invalidation of a target patent, it is necessary to translate the reference document into Chinese for submission. At this time, the reference document needs to be submitted as evidence to the Patent Reexamination and Invalidation Examination Department of CNIPA, and the translation of such a reference document should be accurate, that is, such translation applies to legal document translation, and machine translation combined with human revision could be used.
6. Patent Stability Analysis Stage
After a patent grant, patent stability analysis is sometimes also needed. This process requires a patent stability search. The search process involves translation of patent documents in foreign languages. This situation applies to reference material translation, and machine translation is applicable.
The analysis above can be summarized in the following figures:
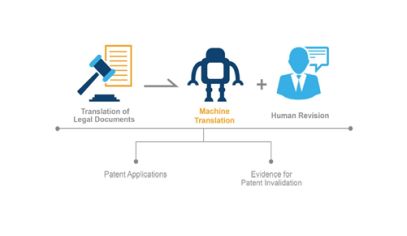
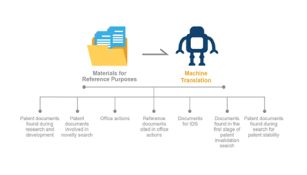
The analysis above shows how to apply machine translation in patent matters. So, how much cost can be saved by using machine translation? How much can efficiency be improved? Let's make a comparison of human translation and machine translation below, for example, if a patent document containing 10,000 Chinese characters is to be translated into English, the translation cost and time required are as follows:
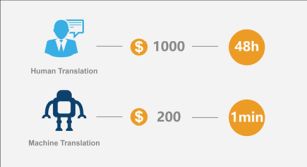
Note: The data about machine translation is obtained from PremiWord Translation ( http://www.premiword.com.cn), the unit price of machine translation being USD 2 per 100 words/characters.
In summary, machine translation helps to effectively reduce cost and increase efficiency. Depending on the translation accuracy requirements, machine translation combined with human revision can be used for legal document translation, and for reference material translation, machine translation is usually enough. We believe that machine translation will be used more widely in patent matters.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

