Further to our earlier articles regarding Indonesia's new investment regime after the enactment of Law 11 of 2020 on Job Creation or Omnibus Law on TMT sector and Hospital businesses, we will now address the key changes on the organization of the public works and public housing construction sectors ("Construction Sector") pursuant to the newly implemented regulations in relation with the Omnibus Law.
The issues that will be assessed in this article includes: (i) the implementation of risk-based business licensing and, (ii) changes to the business licensing regime in the Construction Sector.
Legal Framework: In writing this article, we refer to the following prevailing laws and regulations:
- Government Regulation ("GR") No. 5 of 2021 on the Implementation of Risk-Based Business Licensing ("GR 5/2021"); and
- GR No. 14 of 2021 on the Amendment to GR No. 22 of 2020 on the Implementing Regulation to Law No. 2 of 2017 on the Construction Service ("GR 14/2021" or "Amended GR 22/2020").
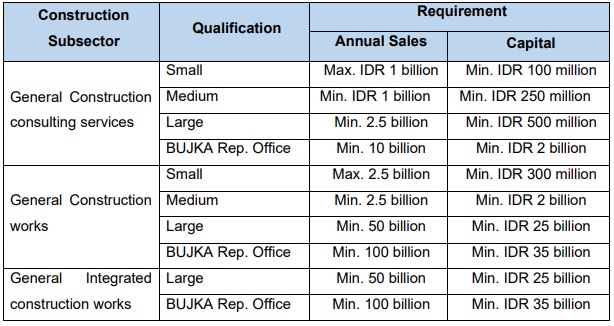
Business Licensing in the Construction Sector: In general, construction business activities are classified into three subsectors i.e., (i) construction consulting services; (ii) construction works; and (iii) integrated construction works (Art. 80 (2) of GR 5/2021). This classifications under GR 5/2021 remains the same as the previous licensing regime.
In addition to the above, the new regulation further classifies the above subsectors into small, medium, large, and large BUJKA Rep Office, in which are categorized based on the assessment on: (i) total annual sales; (ii) total amount of capital; (iii) availability of manpower; and (iv) feasibility to provide construction equipment (Art. 85 of GR 5/2021).
Please see below table for the updated requirement on total annual sales and amount of capital of each construction subsectors pursuant to Art. 90 and 91 of GR 5/2021:
Construction Business Licenses: Pursuant to Art. 81 (1) of GR 5/2021 the applicable licenses to carry out construction business activities within the construction service subsectors are as follows:
- Construction Business Entity Certificates/Sertifikat Badan Usaha ("SBU");
- Construction Working Competency Certificates/Sertifikat Kompetensi Kerja ("SKK");
- Registration of the representative offices of Foreign Construction Service Business Entities/Badan Usaha Jasa Konstruksi Asing ("BUJKA");
- Licensing of Construction Service Business Entity/Badan Usaha Jasa Konstruksi ("BUJK") certification bodies; and
- Licensing of professional construction service certification bodies.
All of the construction business licenses as mentioned in the above shall be applied and issued through the integrated Online Single Submission (OSS) system.
Note: Please refer to: (i) Appendix I of GR 5/2021 for detail information on relevant KBLI, scope of activities, and risk of each construction activity; and (ii) Appendix II of GR 5/2021 for the business licensing requirements of each business activity.
Sustainable Construction Approach: All construction services provider and users are required to implement the sustainable principle, resources, and lifecycles of the building, in each and every stage of construction, starting from general planning until the demolition or the rebuilding phase.
The sustainable construction principle consists of three fundamental points, which are:
- Economically feasible and must be able to improve community welfare;
- Maintaining the environment sustainability; and
- Shall reduce social disparities of the people (Art. 84 (2) of Amended GR 22/2020).
The implementation of the above principles are further governed under Minister of Public Works and Public Housing Regulation No. 9 of 2021.
Contractor Procurement: Pursuant to Art. 72 (2) of Amended GR 22/2020, any procurement of contractor affiliated with construction works for the public interest must be done through a tender, selection, or an electronic catalog. Any violation of such procurement procedure may result in issuance of written reprimand from the relevant government authorities and suspension of construction services.
Standards Fulfillment & Building Failure: GR 14/2021 requires the operation, maintenance, and demolition of a building to comply with the safety, health, and sustainability standard aspects. Otherwise, user and/or the contractor shall be responsible for any building failures caused by non-compliance of such approach (Art. 85 (3) of Amended GR 22/2020).
Transitional Provisions: Upon the enactment of GR 14/2021 on 2 February 2021, the following transitional provisions shall apply:
- construction services which have reached the planning or preparation stage, must immediately comply with GR 14/2021;
- construction services which have reached the implementation stage under GR 22/2020, shall continue until the completion of all the construction services activities;
- design and building work which has reached the planning or preparation stage under GR 22/2020, must be immediately adjusted to GR 14/2021; and
- design and building work which has reached the implementation stage under GR 22/2020, shall continue until the completion of all the construction services activities.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.



