In recent years, the liquidity shortage in the markets, the unexpectedly high increase in raw material costs, the sudden fluctuations in exchange rates, and the problems arising from the deterioration of the supply and demand balance have caused severe economic difficulties for citizens and companies in our country. As a result of this situation, many companies are struggling under the financial burden of debt. As a result of deteriorating cash flow and financial structure, companies have difficulty paying their debts and subsequently encounter many enforcement proceedings and even the risk of bankruptcy. The negative progress in the economy also reveals itself as an increase in execution and bankruptcy files.
THE NUMBER OF ENFORCEMENT AND BANKRUPTCY FILES EXCEEDED 33 MILLION
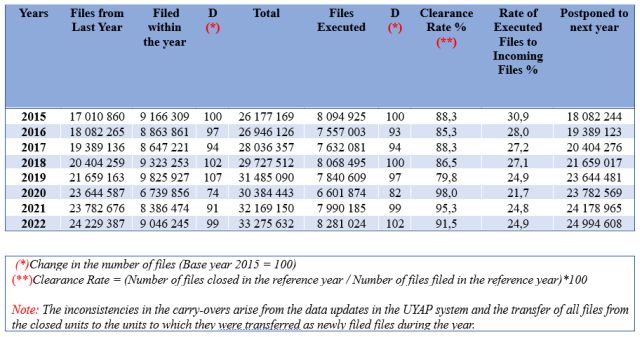
The Ministry of Justice's data on execution and bankruptcy offices again revealed the effects of the deepening economic crisis in Turkiye. According to the compilations made from the data of the Ministry of Justice, In 2022, the number of files in execution and bankruptcy offices reached a total of 33 million 275 thousand 632, including the files carried over from previous years. The increase in the number of execution and bankruptcy files in the 2015-2022 period was 27 percent.
With the Presidential Decree published in March 2020, within the scope of the measures taken to prevent the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic disease, all enforcement and bankruptcy proceedings, except for those for alimony receivables, were suspended. The prohibitions were extended for a while afterward and were removed with the normalization process. Except for the periods of pandemic restrictions and restrictions on execution transactions, there was a significant increase in the number of execution and bankruptcy files in the Execution Offices. With the removal of the prohibition of execution, the number of files escalated again.
In 2022, 9 million 46 thousand 245 new execution and bankruptcy files were filed. With the new files filed in 2022, the total number of execution and bankruptcy files in the offices exceeded 33 million.
The data on the number of files of Execution and Bankruptcy Offices in Turkiye between 2015 and 2022 are as follows:
The Ministry of Justice also shared the distribution of files in execution and bankruptcy offices according to geographical regions. The Marmara Region ranked first with 14 million 659 thousand execution and bankruptcy files. In contrast, in the report, the number of files in the Aegean, Mediterranean, and Central Anatolia regions was 3 million 694 thousand, 3 million 646 thousand, and 4 million 997 thousand, respectively.
NUMBER OF FILES BY TYPE AS OF THE END OF 2022
As of 2022, the total number of files carried over from the previous year is 24,229,387. In 2022, the number of new files filed was 9,046,245, and the number of files closed during the year was 8,281,024. As can be seen from this data, more new enforcement and bankruptcy files are filed yearly than the number of closed files, and the total number of pending files continues to increase rapidly. This is also the situation concerning bankruptcy cases.
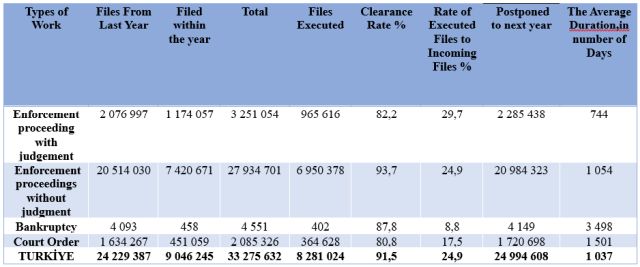
As seen from the table above, the most critical issue distinguishing bankruptcy files from other methods of proceedings is the average duration of bankruptcy proceedings. As of 2022, the average number of bankruptcy proceedings is 3,498 days, 4.70 times more than proceedings with judgment and 3.31 times more than proceedings without judgment. Therefore, there is a necessity for preventive legal arrangements by taking into account the differences in the quality of bankruptcy files.
In order to reduce the workload in the enforcement offices as well as to reduce the rapidly increasing number of files, legal arrangements have been made for the cancellation of debts arising from subscription agreements below a particular figure, as well as for the liquidation of public debts below a specific figure and so forth. However, more arrangements will be needed to make a sufficient difference to reduce the number of enforcement files. In addition to such regulations aiming to reduce the rapid increase in the number of execution and bankruptcy files periodically with temporary solutions, solutions that can permanently solve the problem should be considered.
NUMBER OF BANKRUPTCY FILINGS BY PROVINCES AS OF THE END OF 2022
Upon analyzing the bankruptcy filings among provinces in Turkey as of 2022, a notable correlation emerges between these files and both population size and trade capacity. Istanbul, including 1,599 bankruptcy cases, represents only a third of the total number of bankruptcy cases in Turkey. Ankara is ranked second in terms of file count, with a total of 569 files. Following Ankara, Istanbul has the highest number of files. Izmir ranks third with 233 files, while Antalya, Kocaeli, Bursa, and Denizli have 164, 139, 129, and 113 files respectively. The following table presents comprehensive data regarding the quantity of bankruptcy filings across all provinces.

As seen in the table below, although there are slight changes in the number of bankruptcy files filed between 2015 and 2022, the number of files carried over to the next year is constantly increasing. Considering the long liquidation period in bankruptcy cases and the low collection rate of receivables, creditors often face significant challenges in recovering their receivables in the event of a debtor's bankruptcy. This scenario has the potential to give rise to more economic challenges, akin to a domino effect.

NUMBER OF COMPANIES CLOSED IN THE FIRST HALF OF THE YEAR ACCORDING TO TOBB'S DATA
Based on the statistical data on business closures provided by the Union of Chambers and Commodity Exchanges of Turkiye (TOBB) for June 2023, it is evident that a greater number of companies ceased operations during this month. Consequently, the cumulative figure of closed enterprises reached 9,852 by the end of the first half of the year.
In comparison to the preceding month, there was a 7 percent decline in the number of closed corporations, a 1.4 percent fall in the number of closed cooperatives, and a 12.8 percent reduction in the number of closed real person commercial enterprises. In the month of June 2023, there was a decline of 29.3 percent in the number of closed businesses and a fall of 38.3 percent in the number of closed cooperatives. Conversely, there was an increase of 29.5 percent in the number of closed real person commercial enterprises compared to the corresponding month in 2022.
During the initial half of 2023, in contrast to the corresponding period in 2022, there was a decline of 4.7 percent in the number of closed businesses and a fall of 7.9 percent in the number of closed cooperatives. Conversely, the number of closed real person commercial enterprises witnessed an increase of 16.2 percent.
Based on the data provided by TOBB, it can be observed that a total of 634 firms and cooperatives operating in the areas of wholesale and retail trade, as well as maintenance of motor vehicles and motorcycles, ceased their operations in the month of June. 250 of them are in the manufacturing sector and 223 of them are in the construction sector. Among the real person commercial enterprises closed this month, 1,107 were in wholesale and retail trade and repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles, 392 in construction and 278 in manufacturing sectors.
INCREASE IN BANKRUPTCY FILINGS EXPECTED IN TÜRKİYE
Based on the findings of the Global Insolvency Report by Allianz Trade, a reputable trade receivables insurance firm, which offers supplementary data alongside TOBB statistics, it is projected that bankruptcies in Turkey would witness a 50 percent rise in the current year. Based on the findings of the analysis, a projected rise of 21 percent in global bankruptcies is anticipated for the year 2023, followed by a further increase of 4 percent in 2024.
The Global Insolvency Report published by Allianz Trade highlights the phenomenon of the domino effect in the context of bankruptcy cases;
- The number of bankruptcies for companies with revenues of more than 50 million euros is currently slightly above pre-pandemic levels,
- The most affected sectors are construction, retail and services,
- Low growth, pressure on profitability, and strict financing conditions are testing the resilience of the most vulnerable companies,
- Among these companies, the sectors with the least pricing power are textiles, services, retail, transport, construction, and consumer durables, which are wage-driven and most exposed to interest rate hikes.
However, the recent volatility observed in the banking industry in Europe and the United States prompts an inquiry into the potential consequences of a liquidity crisis on insolvencies. Based on the projections outlined in the paper, it is anticipated that in the event of a financial crisis resembling the one experienced in 2008, the United States and Western Europe may witness a surge in bankruptcy filings, with an estimated rise of 21,600 and 99,900 cases expected in the years 2023 and 2024, respectively. A liquidity crisis of similar scale to what we saw during the bursting of the tech bubble in the early 2000s, as opposed to a substantial financial crisis, would result in an estimated increase of 12,900 and 95,300 insolvencies in the corresponding regions between the years 2023 and 2024. If a credit freeze were to occur, resulting in the absence of new loans, it is anticipated that the number of bankruptcies in the United States and Europe would experience a corresponding increase of 10,700 and 46,300 cases.
CAN THE CONCORDAT SERVE AS A SOLUTION FOR COMPANIES EXPERIENCING FINANCIAL DIFFICULTIES?
The necessity for legal mechanisms to prevent the bankruptcy of companies whose financial structure and cash flows have deteriorated due to the current economic crisis and poor financial management has been increasing recently.
The Bankruptcy Postponement system, formerly incorporated into our legal framework as a final recourse for financially struggling companies prior to bankruptcy, presents several challenges. These include the extended duration of the trial and implementation period, the limited ability of the court to effectively oversee companies undergoing bankruptcy postponement, and the creditors' lack of intervention capabilities within the process.
The "Law No. 7101 on the Amendment of the Enforcement and Bankruptcy Law and Certain Laws," issued in the Official Gazette on 15 March 2018, resulted in the removal of the Bankruptcy Postponement Provisions of the Enforcement and Bankruptcy Law (EBL). The modification in question has resulted in the abolition of the "Postponement of Bankruptcy" provision, while simultaneously introducing an expanded version of the "Concordat" system.
The Concordat is a measure that is typically introduced during periods of economic hardship. Its primary objective is to facilitate the repayment of all regular debts (excluding those that are pledged or privileged) by a debtor. This is achieved through a court-approved payment offer made by the debtor to their creditors. For the offer to be valid, it must be accepted by at least half of the creditors and receive approval from the Commercial Court.
It is an essential advantage for the debtor that it is postponed for an extended period, spread over favorable maturities, and paid equally to all creditors. On the other hand, it is also an essential advantage for the creditor that the firm is saved from bankruptcy, and the debt can be paid.
Although the concordat process, which came to the agenda as a result of the adverse effects of the Covid-19 pandemic on the economy after the high-interest rate and exchange rate crisis in the 2018-2022 period, decreased towards the end of 2022, it started to come to the agenda again due to the economic and financial problems experienced in the first six months of 2023.
In the context of the unfavorable view created by the unpayable and increasing debt burden arising as a result of the execution and bankruptcy files that continue to increase rapidly in our country in recent years, it should be taken into consideration that the aforementioned legal regulations, which are primarily focused on reducing the number of individual and low-amount files and consequently reducing the total number of execution files, are not beneficial for companies.
Since the concordat procedure is relatively new and the companies in the market need to be better informed about it, they do not apply it to the extent necessary for their necessities. As a result, companies that do not enter the concordat process despite their necessities face serious financial difficulties and may even go bankrupt. As a result of bankruptcy, while the commercial activities of the companies are over, their contribution to the economy and the employment they create are also terminated. This situation prevents the creditors from reaching their receivables to a considerable extent.
Bankruptcy liquidation periods are high at this stage; by protecting the companies from many enforcement proceedings and subsequently from bankruptcy, the concordat should be used more actively and efficiently in order for the economy and employment to progress within the framework of stability, and it is a legal solution that companies whose cash flow and financial structure deteriorate in order to improve their financial situation in order not to go into bankruptcy and to obtain the capacity to pay their debts should consider.
The introduction of the Financial Restructuring opportunity in Turkiye was made possible through the implementation of Article 17 of Law No. 7186, which encompasses amendments to the Income Tax Law and Certain Laws. This provision, published in the Repeated Official Gazette No. 30836 on July 19, 2019, added Provisional Article 32 to the Banking Law No. 5411. The primary objective of this regulation is to facilitate the fulfillment of repayment obligations by debtors engaged in credit relations with banks, financial leasing companies, factoring companies, and financing companies in Turkiye. By implementing measures outlined in the framework agreement and contract pertaining to their credit debts with these institutions, debtors are able to not only meet their repayment obligations but also contribute to employment. However, implementing Financial Restructuring Framework Agreements under the Provisional Article 32 of the Banking Law No. 5411 expired on 15.07.2023.
Currently, the concordat is regarded as the most efficient and inclusive method of debt liquidation within our legal framework. It allows creditors to actively participate in the proceedings, ensuring that financially distressed companies with genuine intentions can restore their economic stability and avoid bankruptcy. Moreover, this process provides a secure means for creditors to receive their outstanding debts.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.


