National news coverage on Data Breaches tend to happen in case of what is referred in Cybersecurity as a Catastrophic or Mega Breach i.e. more than 100,000 compromised records. Unfortunately, Data Breaches do not only happen in big-corporates but in all type of organizations, with often disastrous consequences.
In their yearly data breach report, Ponemon Institute/IBM surveyed 500+ organizations having experienced a Data Breach between Feb 2019 and April 2020, in 17 countries, including 26 organizations in Canada.
While the Canadian sample is somewhat limited, the report and associated data points give interesting perspectives on Data Breaches, their costs, contributing factors, and mitigating elements.
The study uses Activity Base Costing to estimate the total cost of a Data Breach by accounting for all internal time spent in dealing with the data breach, external spent, and lost business opportunities.
Headline numbers - Canada:
In 2020, Data Breaches in Canada cost in average CAD 6.3 million, an increase of 6.5% from the year before.
Their cost vs income disproportionally impacted smaller organizations with an average cost of CAD 3.87 million for organizations with less than 500 employees vs CAD +7 million for organizations with more than 5,000 employees.
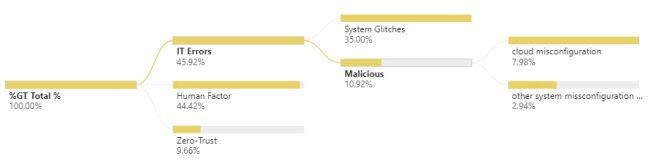
Malicious Attacks were the root cause in 42% of the cases, System Glitches in 35%, and Human Error in 23%
Customer Personally Identifiable Information (PII) were breached in 80% of cases
Lost Business represented 39% of the total cost, Detection, escalation, notification 35%, and Ex-post response 26%
The not so bad news - The Human Factor:
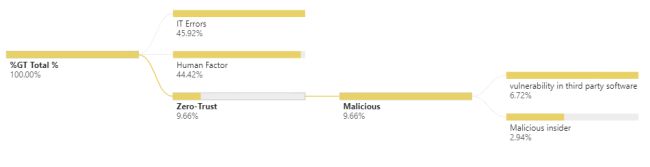
The human factor remains one of the main cause of Data Breaches with 44% of cases.
Half of them relate to the exploitation of employees' behaviour by malicious actors: e.g. phishing, business email compromise, sign-in password compromise, physical compromise (tail-gating)...
The other half categorized as pure human error e.g. leaving a laptop unattended, copying data to an unsecured location...
While representing an important component, it is one of the easiest to comprehend and requires the least complex technical knowledge. Allowing organizations to tackle it through employees training and other safeguards.
Furthermore, organizations that have implemented employee training programmes had, in average, reduced the cost of a data breach by more than CAD 300K -
Making employee training potentially the easiest and most valuable quick win.
The concerning news – IT errors
IT related errors represent 46% of all root causes, being the exploitation of a miss-configured cloud environment (8%) to the more general category of system glitches (35%).
Addressing these root causes requires a higher investment and the drafting of a comprehensive Cyber Security strategy, it may also require an important aspect of change management to modify IT business practices, including the automation of the security management.
As to achieve a proactive vs reactive stance towards emerging cybersecurity risks, organizations can benefit by moving towards a zero-thrust, defensive architecture design. Implementing these types of changes can deliver higher resilience and lower running costs.
Zero – Trust – The remaining cases
Data shows that 7% of all Data Breaches happened through a vulnerability in a Third-Party software and another 3% from a malicious insider.
The later is probably one of the most difficult to protect against, identify and contain. However, the reliance on a Zero-Trust design where no one person can extract a full data set is one of the potentially only way to mitigate the risk.
Unfortunately, the increase in cloud based third party vendors software's has the potential to increase an organization exposure to Data Breaches originating from elements not within their control. A careful third-party software vetting process, contracting clauses and insurance requirements need to be put in place to limit and mitigate this remaining risk.
Summary:
While often not reported by news outlets, Data Breaches happen in small-medium enterprises, with a disproportionate cost vs income in smaller organizations.
Risks and impacts can be efficiently mitigated through the use of an adequate strategy revolving around employee training, Cyber Security strategy and third-party risk management.
Cloud migration and remote staff do result in a documented increase in expected Data Breaches occurrence and cost.
Careful considerations and the definition of a tailored security and authentication framework should be conducted before moving an organization to the cloud, and allowing employees to work remotely.
Where we can help:
CroweMackay has the expertise and experience in reviewing an organization Cyber Security risk profile, proposing strengthening action, and auditing the resulting environment.
Our team has also developed an innovative retro-fitting methodology to strengthen less secure applications and systems without requiring expensive changes.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

